Rational Equations
A rational equation is an equation that contains one or more rational
expressions.
Here are three examples of rational equations.
3
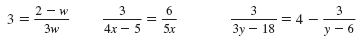
The first step in solving a rational equation is to find the least common
denominator (LCD) of the fractions in the equation.
Procedure
To Find the LCD of the Fractions in an Equation
Step 1 Factor each denominator.
Step 2 List each factor the greatest number of times that it appears
in any one of the denominators.
Step 3 Multiply the factors in the list.
Example 1
Find the LCD of the fractions in this equation:
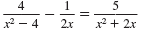
Solution
| Step 1 Factor each denominator.
|
x2 - 4
2x
x2 + 2x |
= (x + 2)(x - 2) = 2 · x
= x(x + 2) |
| Step 2 List each factor the greatest
number of times that it appears
in any one of the denominators.
|
x + 2, x - 2, 2, x |
| Step 3 Multiply the factors in the list. |
2x(x + 2)(x - 2) |
| So, the LCD is 2x(x + 2)(x - 2). |
|