Addition Property of Equality
To solve linear equations in one variable we must use the Basic Properties of Equations:
For any real numbers A, B, C, and D:
1. REFLEXIVE PROPERTY: A = B ⇔ B = A
a) If x = 2 then 2 = x.
b) If x + 3 = 5 then 5 = x + 3
2. ADDITION PROPERTY: If A = B is true then A + C = B + C is true.
a) If x = 2 then x + 5 = 2 + 5
b) If x + 3 = 5 then (x + 3) + (- 3) = 5 + (- 3).
3. TRANSITIVE PROPERTY: If A = B and B = C is true then A = C is true.
[The transitive property is sometimes called the "substitution" property.]
DEFINITION: The solution set for an equation is the set of all numbers that when used is place of
the variable make the equation a true statement.
DEFINITION: Two or more equations with the same solution set are said to be
equivalent equations.
Example:
a) Is x = 3 a solution to 5x – 7 = 18 ?
5(3) – 7 = 18
25 – 7 = 18
18 = 18
b) Is x = 5 a solution to 9x – 8 = 6x + 7 ?
9(5) – 8 = 6(5) + 7
45 – 8 = 30 + 7
37 = 37

We will also apply the Basic Number Properties. In particular,
Use the "Inverse" Property of Addition
a + (-a) = 0
This will be referred to by a "code": Add Opps
Definition of Subtraction:
| → To subtract: |
→ Change to ADD the opposite
|
| |
→ a – b a + (-b) Say a & (-b) |
We can apply these properties "horizontally" one row at a time, as the book does, or
we can apply the properties vertically using a pattern (or balance beam ), where we work on
each side of the equation at the same time. Working vertically helps us to see that we are indeed
"adding the same thing to both sides".
See the following applications working vertically - using the balance beam
2.2a. Constant added on either side: (b, d are letters to represent integers.).
x + b = d or d = x + b
2.2b Find the variable x. To solve the equation we will keep the variable x on that side of the
equation and move the constants to the other side.
To do this we will add opposites on the balance beam below the equation. First look at
the pattern then follow the same steps through the example below.
| Pattern: Add opps:
Complete the step:
Then |
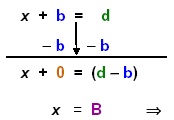 |
|
| Let B = (d – b) the coefficient of x is
1. |
|